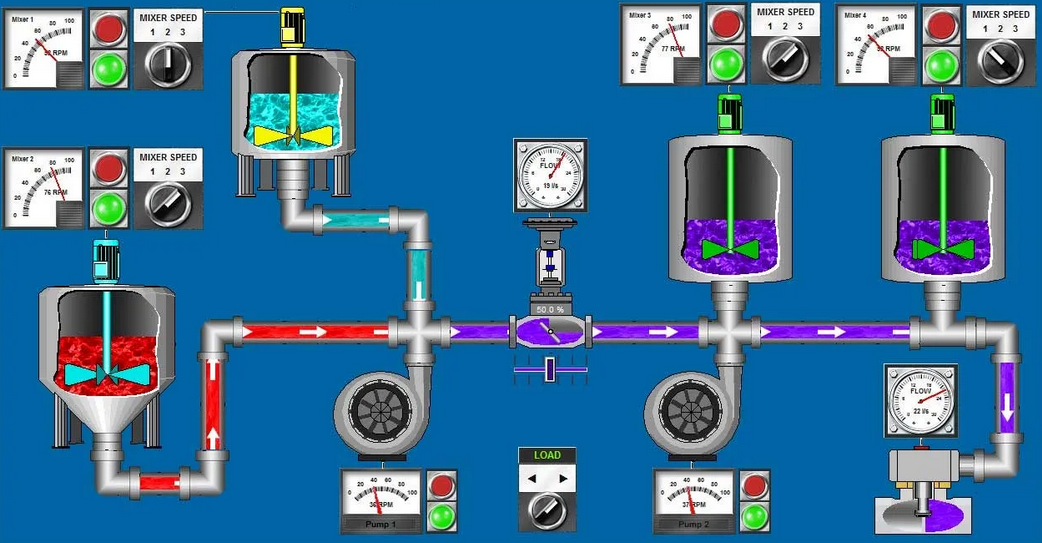
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are a fundamental component of industrial automation. They perform three primary functions: supervision, control, and data acquisition. A SCADA system is part of an architecture that includes one or more computers that perform supervisory functions and implement the human-machine interface (HMI), peripheral devices such as Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), I/O modules, and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) that interface with the process machinery, and a communication network that ensures the correct exchange of data between peripheral devices and supervisory computers.
Real-World Applications of SCADA Systems
SCADA systems are used today in most industrial fields and are an indispensable aid for all companies, regardless of size and sector of activity. They replace humans in carrying out many routine and tedious tasks, which increases productivity, provides faster management of alarms, and reduces the risk of potentially dangerous situations for the environment.
In the utilities sector, SCADA systems are used to manage water treatment and distribution, waste control systems, and electrical power grids. They monitor and control oil and gas pipelines, ensuring safe and efficient operations. In transportation, SCADA systems manage traffic signals, track and locate trains and buses, and control airport baggage handling systems.
In the manufacturing sector, SCADA systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes, including production, fabrication, and assembly lines. They monitor the status of machinery, track production metrics, and control automated processes. In facility management, SCADA systems manage heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, access control systems, and energy consumption monitoring. They are also used in agriculture for irrigation control and monitoring soil moisture levels.
The Advantages of Using SCADA Systems
The use of SCADA systems offers several advantages. They provide a large amount of information, with all system status information, both acquired from the field sensors and provided by real-time control devices (PLC), collected, saved, and made available for further processing, aimed at quality control, efficiency gain, and production optimization.
SCADA systems provide a synthetic and clear picture of the production plant. A series of templates, that are part of the human-machine interface (HMI), provide the operator with a graphical picture of the whole process, its evolution over time, and the unexpected deviations (alarms). By this way, all information relevant to the process is translated into a visual language of easy understanding for the operator.
SCADA systems can grow and adapt easily to the growth of the company. The modular and flexible structure of SCADA software makes it possible to adapt to the different situations that arise when the company needs to grow or change, to respond to the challenges of a globalized market.
Finally, SCADA systems allow centralized control of remote units. Many companies, especially those that manage public service networks (water, electricity, etc.), are characterized by a structure distributed throughout the territory, which traditionally requires the fixed or programmed presence of technical staff for operation and maintenance. The SCADA application ensures remote control of peripheral units and allows technical staff to access all information with a simple browser.
Conclusion
SCADA systems play a crucial role in a wide range of industrial applications. By providing real-time data, enabling control of processes, and facilitating supervision, they drive efficiency, productivity, and safety in modern industries. As such, SCADA systems are not just a tool for industrial automation; they are a key enabling technology for Industry 4.0.
Related Posts
Hi there! I’m Sethu, your go-to guy for all things tech, travel, internet, movies, and business tips. I love sharing insights and stories that make life more interesting. Let’s explore the world together, one article at a time!